Understand the difference between syringe pumps vs. infusion pumps and how to choose the best one for your application.

Topics Covered:
- Syringe Pump vs Infusion Pump Overview
- How Do Syringe and Infusion Pumps Work
- Where Are Syringe and Infusion Pumps Used
- Choosing the Best Infusion or Syringe pump
Syringe Pump vs Infusion Pump Overview
Syringe and infusion pumps are pumping instruments that deliver fluids in a continuous and controlled manner to area−specific targets. In general, syringe pumps are a subset of infusion pumps. Both syringe pumps and infusion pumps offer considerable advantages over manual fluid administration, including dosing exact amounts in small volumes and precise, automated intervals.
In general, both syringes and infusion pumps are useful for minimizing fluid delivery errors in both medical and research applications. The main difference between medical vs. non-medical and IV-style vs. syringe pusher-style is fluid displacement.
What is an Infusion Pump?
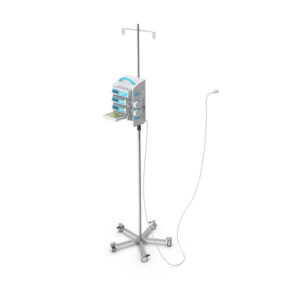
Medical Infusion systems include:
- Bolus Functions
- Occlusion detection (blockage detection)
- Drug libraries for patient use
What is a Syringe Pump?
A syringe pump is a motor-driven device that can dispense precise and accurate quantities of fluid over a specific period of time in advanced research environments. Typically, syringe pumps handle smaller volumes and offer additional programmable features, such as the ability to connect to a computer for data analysis, that infusion pumps do not possess.
Science and industrial syringe pumps systems include:
- Much higher precision than to medical
- Higher Force – 50lbs to 6 TONS of pushing force
- Some designed for Spark and Explosion proof
How do Syringes and Infusion Pumps Work?
Syringe Pump Operation
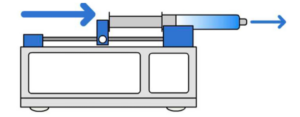
A syringe pump is powered by a motor that can be programmed to gradually drive the plate to push a plunger to administer/eject a specified volume of fluid at a desired flow rate from the syringe to the desired target.
Syringe pumps can operate at very small volumetric flow rates (in micro, nano, and pico metric ranges) while offering pulseless flow with high precision delivery.
Many parameters can be controlled in modern syringe pump applications. For example, pressure control facilitates handling liquids with high viscosity or to introduce fluids under high pressure. Syringe heaters offer temperature control for the syringe. Some syringe pumps allow users to switch between different syringes to regulate the working range.
Infusion Pump Operation
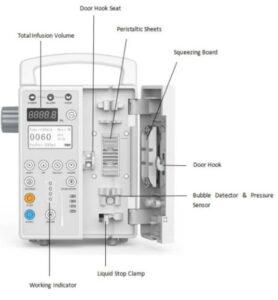
Medical infusion pumps are electronically or mechanically powered by a motor that can be programmed to continuously allow fluid at a specific volume to be administered at a specified rate through a tube to a needless catheter to a patient.
Where are Syringes and Infusion Pumps Used?
Syringe Pumps can be used in a wide range of applications due to their high accuracy and preciseness. Applications that utilize small quantities of fluid that require a specific flow rate, such as material characterization or development in pharmaceutical, chemical, and material sciences research. The advantages of syringe pumps include minimizing volume errors in instrumental analytics for drug delivery, sample delivery, and other microanalyses, such as microfluidics, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and mass spectrometry (MS). They can also be used in research fields that use precise dosing, reagents, and adding minute traces of chemicals during an ongoing experiment.


Infusion Pumps are most commonly used in the clinical industry such as, hospitals, medical centers, retirement facilities, and home care to deliver controlled quantities of medical treatments, nutrients, or blood administration to patients. Occasionally, infusion pumps are utilized to assist in feeding or dosing research animals in biological and medical research.
Several types of infusion pumps exist, including: patient-controlled analgesia (PCA), large volume, elastomeric, enteral, and insulin pumps. Stationary infusion pumps are used at patients’ bedside, while portable and wearable pumps are called ambulatory infusion pumps.

How to Choose a Syringe Pump
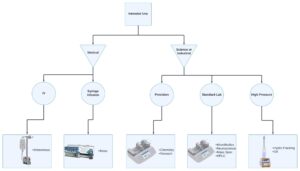
Depending on your industry and specific application, use this flowchart to determine the best pump for your needs with helpful links to where to find them.
- Medical IV Infusion Pumps
- Medical Syringe Infusion Pumps
- Precision Syringe Pumps
- Standard Lab Syringe Pumps
- High Pressure Syringe Pumps